


Next: About this document ...
Problem 1 : An AC voltage generator, whose output is described by
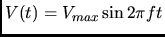 ,
with
,
with
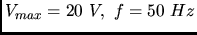 , is connected to an RC circuit where
, is connected to an RC circuit where
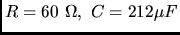 .
What is the current at a time equal to 5.4 periods after t=0 ?
.
What is the current at a time equal to 5.4 periods after t=0 ?
Problem 2 : A radio transmitter broadcasts a signal uniformly in all directions, with a total average
power of 0.8 MW. A receiver needs to see a peak electric field of at least 30 mV/m in order to
detect the broadcast signal. How far can the receiver be from the transmitter and still detect a
signal ?
Problem 3 : If you keep your face 20 cm away from a concave mirror of focal length = 30 cm, how large
will its image be? (assume you have a round face of radius = 12cm). The mirror distance is then
slowly increased from 20 to 40 cm. Describe (in words) what will happen to the image throughout this
motion.
Problem 4 : Your far-sighted brother's has a 50 cm near point and his contact lenses enable him to
see clearly an object as close as 25 cm. If you steal his lens to build a camera, what range must
you allow for the lens-film distances, in order to be able to focus from infinity down to 2 meters?
- Suppose the transmitter of problem 2 broadcasts signals at various frequencies, and you want to
detect preferentially the highest frequency signal. If the wave is traveling along the z-axis, and it
is polarized with the E-field along the x-axis, the best choice for the antenna would be
- a linear antenna parallel to the x-axis
- a linear antenna parallel to the y-axis
- a linear antenna parallel to the z-axis
- a loop antenna parallel to the x-y plane
- a loop antenna parallel to the y-z plane
- a loop antenna parallel to the x-z plane
- The focal length of a plane mirror is
- 0
- equal to the object's distance from the mirror
- equal to minus the object's distance from the mirror
- nonsense, a plane mirror does not have a focal distance
- When transforming sound signals into electric signals and back into sound (e.g. like in an
electric guitar)a spurious, annoying 60 Hz "hum" can be picked up from the AC voltage outlets. The
best way to suppress the spurious signal, without affecting too much the other frequencies (ranging
from a few hundred to a few thousand Hz) is to include in the circuit
- a capacitor
- an inductor
- a resistor
- either a capacitor or an inductor
- any combination of elements that will change the circuit's impedance
- Treating your eye as a lens with an index of refraction = 1.4, what should be the most
appropriate value for its index of refraction if it was to provide clear vision under water?
(
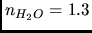 )
)
- 1.08
- 1.50
- 1.82
- 1.97
- nonsense, the lack of clear underwater vision has nothing to do with indices of refraction
- Some trucks carry a warning sign stating "If you don't see my mirrors I don't see you". This
is because of
- the properties of convex mirrors
- the properties of concave mirrors
- the laws of reflection
- the laws of refraction
- the magnification equation
Problem 1 : Your radio receives the signals from two different stations, whose frequencies differ
by 10 MHz. To pick up the signal from the higher frequency station, you tune your radio RLC serial
circuit to resonance by setting L = 2 nH and C = 2 nF. If the signals from both stations induce the
same
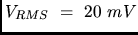 , and the current from the station at resonance is
, and the current from the station at resonance is
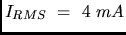 , what is
the RMS current due to the lower frequency station?
, what is
the RMS current due to the lower frequency station?
Problem 2 : You want to design a solar powered electricity generator for equatorial Africa. Here is the
data available to you : sun total power:
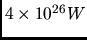 , emitted uniformly in all directions;
average sun-earth distance :
, emitted uniformly in all directions;
average sun-earth distance :
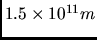 ; angle of earth rotation axis with plane of the
orbit:
; angle of earth rotation axis with plane of the
orbit: 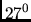 (see picture); efficiency of solar cells for converting solar energy into electric
energy : 40%. How big an area you need to instrument with solar cells in order to get a 500 kW output
when the sun is shining?
(see picture); efficiency of solar cells for converting solar energy into electric
energy : 40%. How big an area you need to instrument with solar cells in order to get a 500 kW output
when the sun is shining?
Problem 3 : A car plunges into the sea, and the image of a fish located 25 cm from the car's convex
rearview mirror is 3 times smaller than the fish itself. What is the mirror's focal length?
(
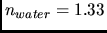 )
)
Problem 4 : A mildly far-sighted person, Near Point at 40 cm, Far Point at infinity, asks for a contact
lens prescription that will allow him to see clearly objects at 30 cm from his eyes. The careless optician
prepares a set of lenses with the correct magnitude but the wrong sign for the lenses focal distance.
What will the person's range of vision be when wearing those contacts?
- If the AC circuit whose voltage and current are sketched below contains only one element, it must
be
- a capacitor
- an inductor
- a resistor
- either a capacitor or an inductor
- not enough information
- A converging lens and a concave mirror are positioned facing each other, so that their foci
coincide. When rays parallel to the lens axis cross the lens, are reflected by the mirror and cross the
lens again, the final direction of the rays will be
- parallel to the incoming rays
- converging towards the lens focus to the right of the lens
- diverging, with thteir extensions meeting at the lens/mirror focus
- not enough information
- none of the above
- To change light polarized in the vertical direction into light polarized in the horizontal
direction, you will get the largest transmitted intensity by using two polarizers
- both oriented horizontally
- one oriented horizontally, the other vertically
- one oriented at 45 degrees to the horizontal, the other horizontally
- one oriented at 30 degrees to the horizontal,the other horizontally
- none of the above would work
- A periscope is made with two plane mirrors tilted at 45 degrees. The produced image is
- inverted, real
- upright, real
- inverted, virtual
- upright, virtual
- not enough information
- To make an optical fiber you have the choice of 5 different materials, with indices of refraction
respectively 1.2, 1.4, 1.6, 1.8 and 2.0. In order to maximize light collection and transmission, which
pair would be the best choice for the fiber's core and cladding ? (specify which is which)



Next: About this document ...
Sergio Conetti
2003-04-01