![]()
![]()
![]()
If an equation you need is not listed here, ask.
PHYS 231 Quiz #1
Cheat Sheet: ¯¯
¯
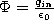
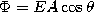
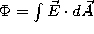
If an equation you need is not listed here, ask.
Multiple choice: 1 pt. each
1. Which of the following is always true about the force of one charge on another?
A. If the electric force is nonzero, then it is attractive.
B. The greater the distance between the charges, the greater the electric force.
C. The gravitational force is comparable to the electric force.
* D. The electric force is zero if either charge is zero.
2. Which is true about electric fields in general?
* A. An electric field can exist in a region where there is no charge.
B. The electric field at a point depends on the test charge at that point.
C. Electric field lines always point away from point charges.
D. The electric field at a point in space is a scalar value.
3. Positive charge is distributed on the surface of a conducting sphere. The total flux through a surface contained entirely within the sphere is
A. positive
* B. zero
C. negative
D. Not enough information given. We need to know the shape of the surface.
4. A good Gaussian surface to choose to calculate the electric field around a line charge is
A. a sphere
B. a cube
* C. a cylinder
D. a plane
5. A negatively charged rubber rod is brought close to a fixed conducting sphere. While the rod is close by, the side of the sphere opposite to the rod is touched by a student (acting as a ground). If the students finger is removed and then the rod is removed, what charge remains on the sphere?
* A. Positive
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. Not enough information given.
6. The total flux through a surface is negative. What can we conclude about the inside of the surface?
A. Only positive charges reside inside the surface.
B. Only negative charges reside inside the surface.
C. Charge is distributed evenly inside the surface.
* D. None of the above.
7. Draw the electric field lines around the two charges below.(4 pts)
Extra Credit (1 pt): How is it possible that a negatively charged balloon can stick to a neutral wall?
The negative charge of the balloon induces a positive charge on the surface of the wall. This positive charge attracts the negative charge of the balloon.