- The thermal resistivity
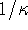 is, by definition, the inverse of
the thermal conductivity
is, by definition, the inverse of
the thermal conductivity  . What are the SI units for thermal
resistivity?
. What are the SI units for thermal
resistivity? - Find the heat current flowing through a slab of thickness 2.5 cm (1 inch) and area 1 square meter (9.3 square feet) when there is temperature difference of 5 kelvin (9°F) across the slab.
- The R value is by definition the thickness times the thermal resistivity (it is not to be confused with the thermal resistance, which is thickness times thermal resistivity divided by surface area). In customary US units, R values are quoted in °F×hr×ft2/Btu. If R = 1 in US customary units, what is its value in SI units?
- A room has outside walls on two sides. If the inside temperature is 20°C and the outside temperature is 30°C, how long will it be before the inside air temperature raises to 21°C (assuming that only the air gets heated and there are no leaks)? You are expected to supply typical room dimensions as well as the specific heat of air. Give a numerical answer for walls with (average) R = 1 US unit, which is very poor insulation (but it is difficult to get R as high as 10) and show how the result scales with R.
- How does your result change if all room dimensions are doubled? If the floor area is doubled but the height stays the same?
- Optional for those who like math: how long before the inside air temperature rises to 25°C ? To 29°C? (For a rough answer: take the result of part (5) and multiply by 5, and by 10.)
- Actually, heat is also transferred to furnishings, floor, ceiling, and the other walls. Most solids have about the same specific heat (what is it?), so you can estimate how long it will really take before the temperature raises to 21°C if you assume that all surfaces also warm up to a depth of 1 cm, effectively.
- Neglecting the fact that the inside temperature is slowly rising, make an accurate sketch of the temperature profile and the heat current within an outer wall, assuming that it is just a slab of thickness 2.5 cm (you do not need MAPLE for this). Show explicitly that the continuity equation, the Fourier equation and the diffusion equation are satisfied by your sketch.
- Length. What is its magnitude? What does it represent physically?
- Magnetic moment. What is its magnitude? What does it represent physically?
- Resistance. What is its magnitude? (You might want to look up the quantum Hall effect.)
- Magnetic flux. What is its magnitude? (Try to have a look at quantized flux in superconductors.)
- Length. What is its magnitude? What does it represent physically? Could you have constructed such a quantity without Planck's constant?
- Time. What is its magnitude?
- Mass. What is its magnitude?