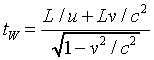
Michael Fowler
University of Virginia
Physics 252 Home Page
Previous lecture
If I walk from the back to the front of a train at 3 m.p.h., and
the train is traveling at 60 m.p.h., then my speed relative to
the ground is 63 m.p.h. As we have seen, this obvious truth, the
addition of velocities, follows from the Galilean transformations.
Unfortunately, it can't be quite right for high speeds. We know
that for a flash of light going from the back of the train to
the front, the speed of the light relative to the ground is exactly
the same as its speed relative to the train, not 60 m.p.h. different.
Hence it is necessary to do a careful analysis of a fairly speedy
person moving from the back of the train to the front as viewed
from the ground, to see how velocities really add.
We consider our standard train of length L moving down
the track at steady speed v, and equipped with synchronized
clocks at the back and the front. The walker sets off from the
back of the train when that clock reads zero. Assuming a steady
walking speed of u meters per second (relative to the train,
of course), the walker will see the front clock to read L/u
seconds on arrival there.
How does this look from the ground? The ground observer sees the walker reach the front clock when it reads L/u, but at this instant the ground observer says the back clock, where the walker began, reads L/u + Lv/c2. Recalling also that the ground observer sees all the train clocks to be running slow by the time dilation factor, the walk takes a time, measured from the ground
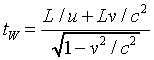
How far does the walker move as viewed from the ground? In the time tW, the train travels a distance vtW, so the walker moves this distance plus the length of the train, remembering that the train is contracted as viewed from the ground, so the distance covered relative to the ground during the walk
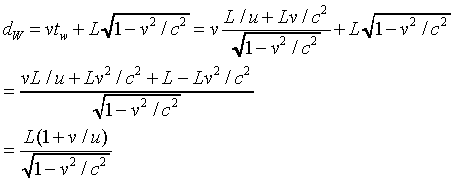
The walker's speed relative to the ground is simply dW/tW, easily found from the above expressions:
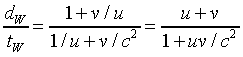
This is the appropriate formula for adding velocities. Note that
it gives the correct answer, u + v, in the low velocity
limit, and also if u or v equals c, the sum
of the velocities is c.
Exercise 1. The direct derivation given above is really
equivalent to a rederivation of the Lorentz equations. The equation
describing the walker's path on the train is just x' = ut'.
Substitute this in the Lorentz equations and prove it leads to
a path relative to the ground given by x = wt, with w
given by the velocity addition formula.
Exercise 2. Suppose a spaceship is equipped with a series
of one-shot rockets, each of which can accelerate the ship to
c/2 from rest. It uses one rocket to leave the solar system
(ignore gravity here) and is then traveling at c/2 (relative
to us) in deep space. It now fires its second rocket, keeping
the same direction. Find how fast it is moving relative to us.
It now fires the third rocket, keeping the same direction. Find
its new speed. Can you draw any general conclusions from your
results?
Imagine now a rather wide train, of width w, and the walker
begins the walk across the train, which is now equipped with clocks
on both sides, when the clock where he begins reads t =
0. For walking speed uy' (across the train is
the y-direction) when he reaches the clock at the other
side it will read w/uy'. How is this
seen from the ground? The width of the train w will be
the same, there is no Lorentz contraction in the y-direction
for motion in the x-direction. The beginning and ending
clocks will also be synchronized as seen from the ground, since
they are separated in the y-direction but not the x-direction.
However, they are clocks moving at relativistic speed, so they
will exhibit the familiar time dilation factor. That is, when
they read w/uy', a clock on the ground
will read
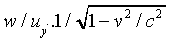
Thus, as observed from the ground, walking directly across the
train is slowed down by the time dilation factor, just as is every
other activity on the train as seen from the ground.
However, for steady motion on the train in an arbitrary direction
(ux', uy') the cross-train
velocity transforms in a more complicated way, because the train
clocks at the beginning and end of the walk are now separated
in the x-direction, so if they register an elapsed time
of w/uy a ground observer would add a
lack of synchronicity term
Thus the time for the walk as observed from the ground
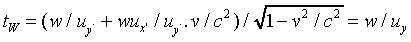
From this we find the general formula for transformation of transverse
velocities:
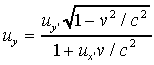
For the special case of walking directly across the train, ux' = 0, we recover the earlier result, that transverse velocity is simply slowed by the time dilation effect.
Actually, the first test of the addition of velocities formula was carried out in the 1850's! Two French physicists, Fizeau and Foucault, measured the speed of light in water, and found it to be c/n, where n is the refractive index of water, about 1.33. (This was the result predicted by the wave theory of light.)
They then measured the speed of light (relative to the ground) in moving water, by sending light down a long pipe with water flowing through it at speed v. They discovered that the speed relative to the ground was not just v + c/n, but had an extra term, v + c/n - v/n2. Their (incorrect) explanation was that the light was a complicated combination of waves in the water and waves in the aether, and the moving water was only partially dragging the aether along with it, so the light didn't get the full speed v of the water added to its original speed c/n.
The true explanation of the extra term is much simpler - velocities don't simply add. To add the velocity v to the velocity c/n, we must use the addition of velocities formula above, which gives the light velocity relative to the ground to be:
Now, v is much smaller than c or c/n, so 1/(1 + v/nc) can be written as (1 - v/nc), giving:
Multiplying this out gives v + c/n - v/n2 -v/n.v/c, and the last term is smaller than v by a factor v/c, so is clearly negligible.
Therefore, the 1850 experiment looking for "aether drag" in fact confirms the relativistic addition of velocities formula! Of course, there are many other confirmations. For example, any velocity added to c still gives c. Also, it indicates that the speed of light is a speed limit for all objects, a topic we shall examine more carefully in the next lecture.
Physics 252 Home Page
link to next lecture
Copyright © Michael Fowler 1997